Contents
Overview
This section explains how to change the scale.
There are some restrictions on the scale while editing, and on changing the scale while in progress.
Limitations
First, it’s important to note that only uniform scaling is supported.
That is, global scaling of the X, Y and Z axes by a uniform factor of 2x, 3x, 0.5x, etc.
It is not possible to scale the X, Y and Z axes independently.
There are also the following limitations on scale changes during editing and at run time:
Editing Scale
The scale must be uniform and positive while editing.
Negative scale is not allowed.
The Inspector will display an warning message if the component is improperly scaled.
Running Scale
You can freely change the scale as long as it is uniform during execution.
Also, from v2.8.0, negative scale is also supported while running.
By making the scale negative, you can invert the entire character.
This is mainly useful for 2D games.
However, there is a restriction that only one axis, XYZ, can be set to negative scale.
Base scale
The scale value at which the cloth component is initialized at runtime is called the base scale.
MagicaCloth’s scale change is a little special, so that no matter what scale change you make at runtime, it will not change its base scale and how it sways.
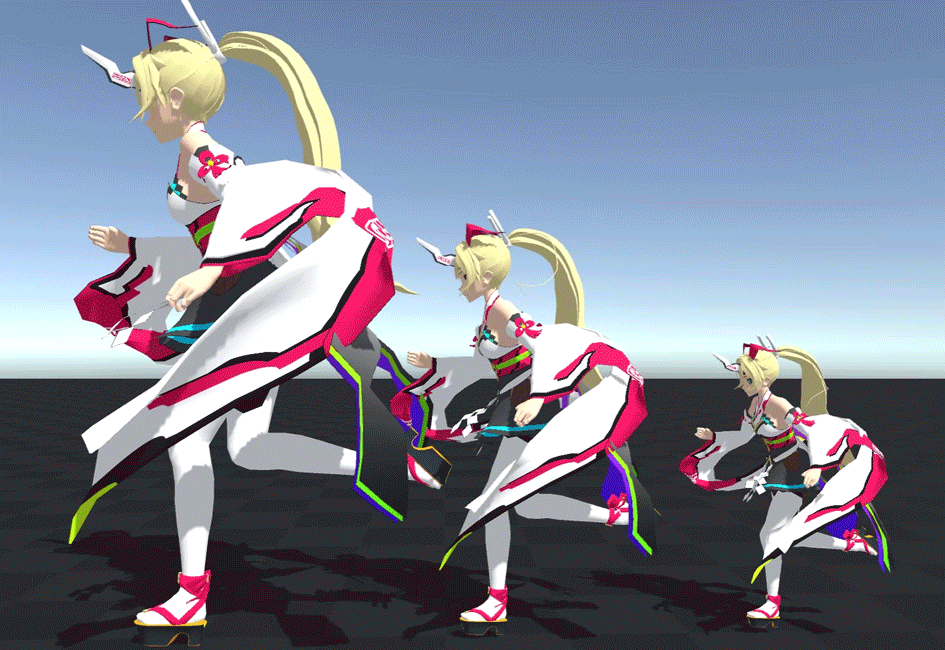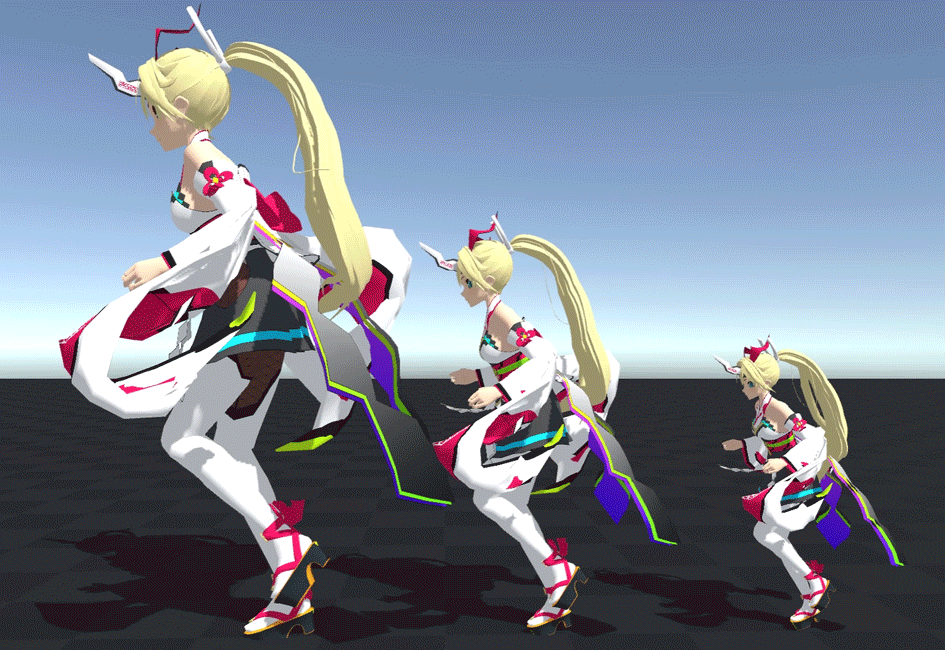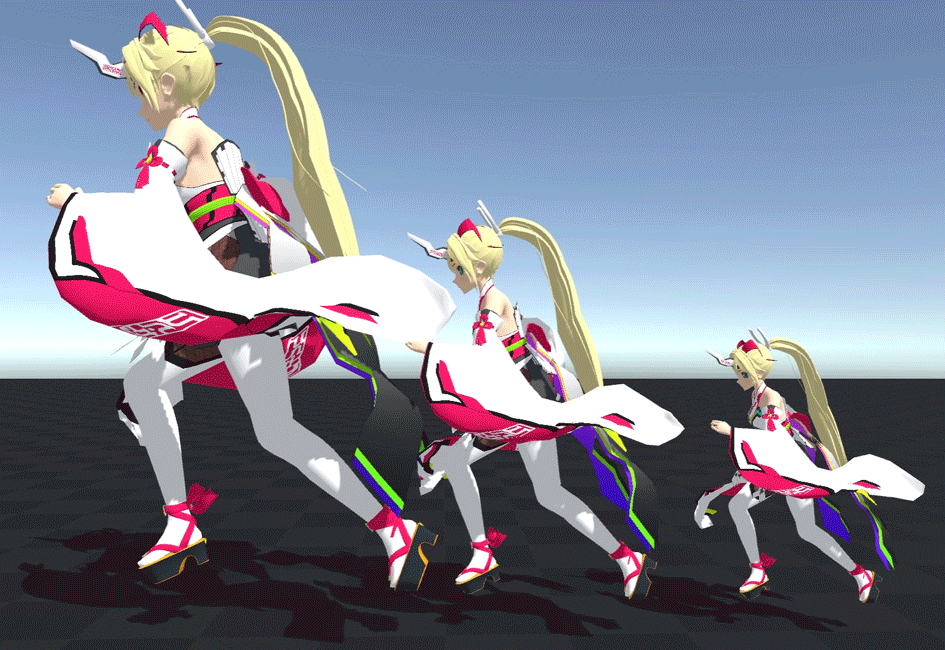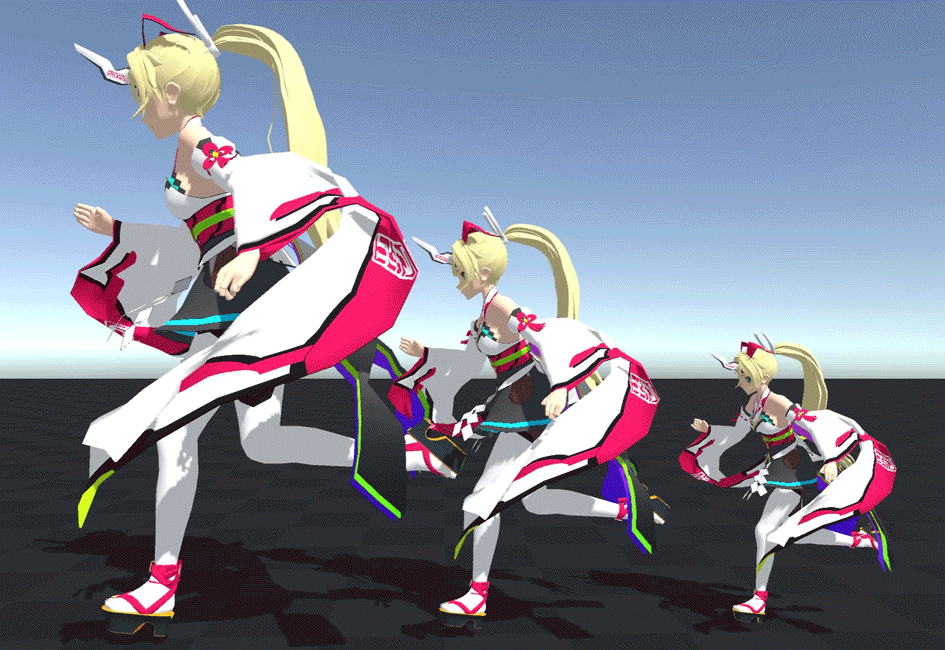
For example, the following three characters are centered at base scale, left at 1.5x, and right at 0.7x.
You can see that the shaking is exactly the same even if the size changes.
As you can see, the scale at initialization is very important.
Notes on scale changes
There are some limitations when scaling characters on the fly.
However, these limitations can be worked around in v2.13.0 and later, or by using pre-building.
See Character Instantiation for more information.
The following limitations apply only when using runtime builds prior to v2.13.0.
Cannot scale before initialization
Scale changes at runtime must be made after cloth components are initialized.
Changing scale before initialization will result in unintended behavior.
Cloth components are basically initialized in Start(), and the reference scale is recorded at this time.
Therefore, if you want to change scale before Start() for some reason, you will need to call initialization manually.
Use Initialize() for this.
Precautions when placing in the scene in advance
For example, let’s say you have a character prefab A with a cloth component.
Please note that if you place this prefab A in the scene from the beginning with the scale doubled, it will not work well.
This is because the base scale is determined at the time of initialization, so this character will be treated as the base scale when the scale is doubled.
In such a case, it is necessary to place it in the scene without changing the scale, and change the scale after initializing the component with a script or the like.